Choosing the Best Processor in Laptop a Practical Guide

If you've ever wondered what makes one laptop feel lightning-fast while another chugs along, the answer usually starts with the processor. Officially called the CPU (Central Processing Unit), this tiny silicon chip is, without exaggeration, the brain of the entire operation. It's the engine that powers everything you do, from clicking open a browser to rendering a complex 4K video.
Simply put, a better processor means a faster, smoother, and more capable laptop.
What a Laptop Processor Actually Does
Imagine your laptop’s processor as the head chef in a high-end restaurant kitchen. Every time you launch an app, type a sentence, or even move your mouse, you're sending an order to the kitchen. The processor is that chef, instantly reading the order, grabbing the necessary data (the ingredients), following the instructions (the recipe), and executing the task perfectly.
A really good processor is like a world-class chef who can juggle dozens of complicated orders at once without breaking a sweat. This is why a powerful CPU makes multitasking feel so effortless—letting you stream music, hop between 20 browser tabs, and run a demanding application all at the same time without any frustrating lag.
From Simple Instructions to Complex Tasks
At its most fundamental level, a processor is just a machine for executing billions of simple instructions every single second. These tiny operations—fetching data from memory, decoding it, carrying out the command, and writing back the result—are the building blocks for everything your computer does.
This entire cycle happens at mind-boggling speeds, measured in gigahertz (GHz). When you do something complex, like applying a filter in Photoshop, the processor is actually executing millions of these tiny instructions in a highly coordinated sequence. How efficiently and quickly it blitzes through this workflow is what you perceive as your laptop’s overall performance.
The Core of Performance: The quality of the processor is arguably the single most important factor dictating a laptop’s speed and capability. A premium CPU can make an otherwise average laptop feel snappy, while a budget processor will bottleneck even the best supporting components.
Managing Heat and Efficiency
All this high-speed work generates a serious amount of heat. If that heat isn't managed effectively, it can damage the processor and force it to slow down to protect itself—a phenomenon known as thermal throttling. This is where cooling systems, fans, and crucial components like thermal paste come into the picture. Keeping things cool is vital for performance, which is why it's good to understand the basics of things like maintaining CPU thermal paste.
Ultimately, the processor sets the ceiling for your laptop's potential. It defines how quickly it boots up, how smoothly it runs demanding software, and how well it handles your daily grind. Getting your head around its role is the first—and most important—step to choosing the right machine.
Now that we know what a processor does, let's look at how its performance translates to the things you actually do every day.
How a Processor Impacts Your Daily Laptop Use
This table gives a quick summary of how processor quality affects common laptop activities, helping you connect the technical specs to real-world results.
| Your Activity | What the Processor Handles | Why a Better CPU Improves It |
|---|---|---|
| Web Browsing | Loading pages, running scripts, and managing multiple tabs. | A faster CPU loads complex sites instantly and keeps the experience smooth, even with dozens of tabs open. |
| Office & Productivity | Running spreadsheets, creating presentations, and video conferencing. | A stronger processor crunches spreadsheet data faster, prevents lag during video calls, and makes multitasking seamless. |
| Content Creation | Editing photos, rendering videos, and working with large design files. | More cores and higher speeds drastically cut down rendering times and allow for real-time previews without stuttering. |
| Software Development | Compiling code, running virtual machines, and managing local servers. | A powerful CPU compiles code in seconds instead of minutes, making the entire development cycle much more efficient. |
| Gaming | Processing game logic, AI, physics, and sending instructions to the GPU. | A high-performance CPU prevents bottlenecks, ensuring higher frame rates and a smoother, more responsive gaming experience. |
As you can see, nearly every task benefits from a better processor, but the impact is most dramatic in demanding workloads like gaming, content creation, and development.
Decoding Processor Specs Like a Pro

Diving into a laptop's technical specifications can feel like trying to read a foreign language. Terms like cores, GHz, and cache are thrown around constantly, but what do they actually mean for you?
Luckily, you don't need a computer science degree to figure this out. Once you get a handle on a few key concepts, you can look at any spec sheet and know exactly what you’re getting. Think of it this way: you don't need to be a mechanic to know what makes a car fast. The same logic applies here; a handful of core metrics tell most of the story.
Let's break down the essential terms into simple, practical ideas, so you can compare models with confidence.
Cores and Threads: The Multitasking Team
The first spec you’ll almost always see is the number of cores and threads. The easiest way to think about this is to imagine each core as an individual worker dedicated to handling tasks. A dual-core processor has two of these workers, while an octa-core processor has eight.
It's pretty straightforward: more workers mean more jobs can be handled at the same time. This is why a processor with more cores is a multitasking powerhouse, easily juggling a virus scan in the background while you’re on a video call and editing a document.
Threads are a bit more abstract, but they’re just as important. Think of a thread as a virtual helper that allows a physical core to manage its workload more efficiently. A core can often handle two threads at once, letting it switch between different instructions more fluidly. So, a processor with 8 cores and 16 threads can manage sixteen separate instruction streams simultaneously—a massive boost for demanding software like video editors and modern games.
Clock Speed: The Pace of Work
If cores are the workers, then clock speed is how fast each of them works. It’s measured in gigahertz (GHz) and represents the number of cycles a processor can execute every second. A 3.0 GHz processor, for example, performs three billion cycles in that tiny timeframe.
Generally, a higher clock speed means faster performance for single-threaded tasks—actions that rely on the raw speed of a single core. A lot of software, particularly older programs and some games, still depends heavily on one core moving quickly to feel responsive.
But hold on. A higher clock speed doesn't automatically make a processor better. A modern chip with a lower clock speed can often run circles around an older one with a higher clock speed, all thanks to improvements in its design. This brings us to architecture.
Architecture: The Blueprint for Efficiency
Architecture is the fundamental design of the processor. Think of it as the difference between an old, clunky factory layout and a modern, automated one. Even if both factories have the same number of workers (cores) working at the same pace (clock speed), the modern one will produce far more because its design is just smarter.
Each new generation of processors brings architectural improvements, allowing them to do more work per clock cycle. This is precisely why a new Intel Core i5 might outperform an older Core i7, even if the older chip has a higher GHz rating on paper. When comparing processors, always consider the generation—newer is almost always better. This continuous improvement is central to the computer manufacturing industry, which continues to show resilience. For instance, the Dutch computer and peripheral equipment manufacturing sector achieved a 4.5% compound annual growth rate between 2020 and 2025, with major brands like HP and Dell dominating the market.
Cache: The High-Speed Toolbox
Cache is a small amount of super-fast memory built right into the processor chip itself. It acts like a chef's countertop, holding the most frequently used tools and ingredients (data) for immediate access.
Instead of the processor having to go all the way to the main kitchen storage (the laptop's RAM), it can just grab what it needs from the cache instantly. This simple trick drastically speeds up repetitive tasks and makes the entire system feel much snappier.
Key Takeaway: A larger cache (measured in megabytes, or MB) lets the processor store more data close at hand. This reduces delays and improves overall performance, especially in data-heavy tasks like gaming or database work.
TDP: Power and Heat Management
Finally, there’s Thermal Design Power (TDP), a crucial but often overlooked metric. Measured in watts (W), it tells you the maximum amount of heat a processor is expected to generate under a heavy workload. In essence, it’s a proxy for how much power the chip consumes and, importantly, how much cooling it's going to need.
This spec is especially important for the processor in a laptop, where space and cooling are always at a premium.
- Low TDP (e.g., 15W): These processors are made for thin-and-light laptops. They sip power, generate less heat, and give you much longer battery life, but they can't sustain peak performance for long.
- High TDP (e.g., 45W+): You'll find these in chunky gaming laptops and mobile workstations. They deliver serious power for demanding tasks but require beefy cooling systems and will drain the battery in no time.
Understanding TDP helps you match a laptop's physical design with its intended use. A sleek ultrabook with a high-TDP chip would likely overheat and throttle, while a bulky gaming rig with a low-TDP chip would just be underpowered. Advancements in processor architecture are also shaping the capabilities of modern AI; our article unpacks what the new Gemini 3 benchmark achieves.
Comparing the Processor Giants: Intel, AMD, and Apple
When you start shopping for a new laptop, you’ll quickly find the processor market is a three-horse race between Intel, AMD, and Apple. For decades, Intel and AMD were locked in a fierce rivalry, a constant back-and-forth that pushed both companies to build faster, more efficient chips. But recently, Apple threw a massive wrench in the works by designing its own processors, completely changing the game for performance and battery life.
Figuring out the unique philosophies and strengths of each brand is the key to getting the right laptop. This isn't about picking a favourite team; it’s about matching a processor's core advantages to the work you actually do.
Intel: The Established Industry Leader
For the longest time, Intel was the undisputed king. Its Core series—the i3, i5, i7, and i9—became a household name, synonymous with reliable computing. Intel’s strength has always been its solid performance, incredible compatibility with just about all software and hardware, and its sheer presence across almost every laptop brand out there.
Intel processors are particularly known for their powerful single-core performance. This makes them fantastic for tasks that lean heavily on the raw speed of one core, which includes a lot of games and everyday apps. They offer a massive range of chips, from the power-sipping U-series in ultrabooks to the beefy H-series designed for mobile workstations and serious gaming rigs.
- Key Strength: Excellent single-core speed and wide market availability.
- Best For: General productivity, business users, and gamers who value high clock speeds.
- Naming Scheme: Follows the Core i3 (entry-level), i5 (mainstream), i7 (high-performance), and i9 (enthusiast) structure.
AMD: The Resurgent Competitor
AMD's Ryzen processors pulled off one of the biggest comebacks in tech history. For years, AMD was seen as the budget option, but with the launch of its Ryzen architecture, it started challenging—and often beating—Intel on pure performance.
AMD's secret weapon is its multi-core strength. Ryzen chips frequently pack more cores and threads at similar price points, making them absolute beasts at multitasking and heavy creative workloads like video rendering, 3D modelling, and compiling code. A processor like the Ryzen 5 6600H, for example, can deliver multi-core scores that leave older Intel chips in the dust.
AMD's focus on multi-core performance has made Ryzen processors a favourite among content creators, developers, and anyone who juggles multiple heavy applications at once. They offer a compelling mix of raw power and great value.
On top of that, AMD's integrated graphics have consistently been a step ahead of Intel's, giving you a much better out-of-the-box experience for light gaming without needing a separate graphics card.
Apple: The Efficiency Revolution
Apple took a massive leap by ditching Intel and creating its own Apple Silicon—the M-series chips. These processors are built on an ARM-based architecture, similar to what’s in your iPhone, and they were designed with one goal in mind: maximum performance per watt.
The result is a chip that delivers incredible speed while sipping power. This is how MacBooks can handle demanding tasks like 4K video editing and graphic design while boasting a battery that genuinely lasts all day. By putting the CPU, GPU, and memory into a single package (a System on a Chip, or SoC), Apple achieved a level of optimisation that traditional PC laptops still struggle to match. You can dive deeper in our guide on exploring the power of Mac computers with Apple Silicon.
- Key Strength: Unmatched power efficiency, leading to incredible battery life and cool, quiet operation.
- Best For: Creative professionals, students, and anyone who puts battery life and a seamless experience first.
- Naming Scheme: Follows the M1, M2, M3 series, with Pro, Max, and Ultra versions for even higher performance.
To see how these processor choices play out in real-world performance, a detailed MacBook Air vs MacBook Pro comparison can be incredibly insightful.
Intel vs AMD vs Apple Processor Comparison
Here’s a head-to-head breakdown of the major processor brands to help you identify the best fit for your workflow and budget.
| Characteristic | Intel Core Series | AMD Ryzen Series | Apple M-Series |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Strong single-core performance and wide compatibility. | Excellent multi-core performance and value. | Superior power efficiency and ecosystem integration. |
| Ideal User | Business users, mainstream gamers, general productivity. | Content creators, multitaskers, budget-conscious gamers. | Creative professionals, students, users valuing battery life. |
| Typical Naming | Core i3, i5, i7, i9 | Ryzen 3, 5, 7, 9 | M1, M2, M3 (Pro, Max, Ultra) |
| Integrated Graphics | Good for daily use (Intel Iris Xe). | Generally stronger, better for light gaming. | Very powerful, suitable for creative work. |
| Power Consumption | Varies widely, with H-series being power-hungry. | Generally competitive, often more efficient in multi-core tasks. | Exceptionally low, leading to industry-best battery life. |
In the end, there’s no single "best" brand for everyone. Intel offers a reliable and massive selection for almost any need. AMD brings incredible multi-core power for the money. And Apple delivers a beautifully optimised experience built around efficiency. The right choice depends entirely on what you value most.
Matching Your Processor to Your Real-World Needs
All those technical specifications are just numbers on a page until you connect them to what you actually do every day. The best processor isn't always the priciest one; it's the one that clicks perfectly with your tasks, habits, and workflow. A writer paying a premium for a top-tier gaming CPU is like a city commuter buying a Formula 1 car—sure, the power is there, but it’s going completely to waste.
This section is all about translating abstract metrics like cores, threads, and clock speeds into tangible, real-world performance. We'll walk through different types of users to help you figure out which processor specs you should actually care about, ensuring your money goes toward performance you'll genuinely feel.
This decision tree can give you a quick steer on which processor family might be the best starting point, depending on whether your main goal is raw performance, battery efficiency, or getting the most bang for your buck.
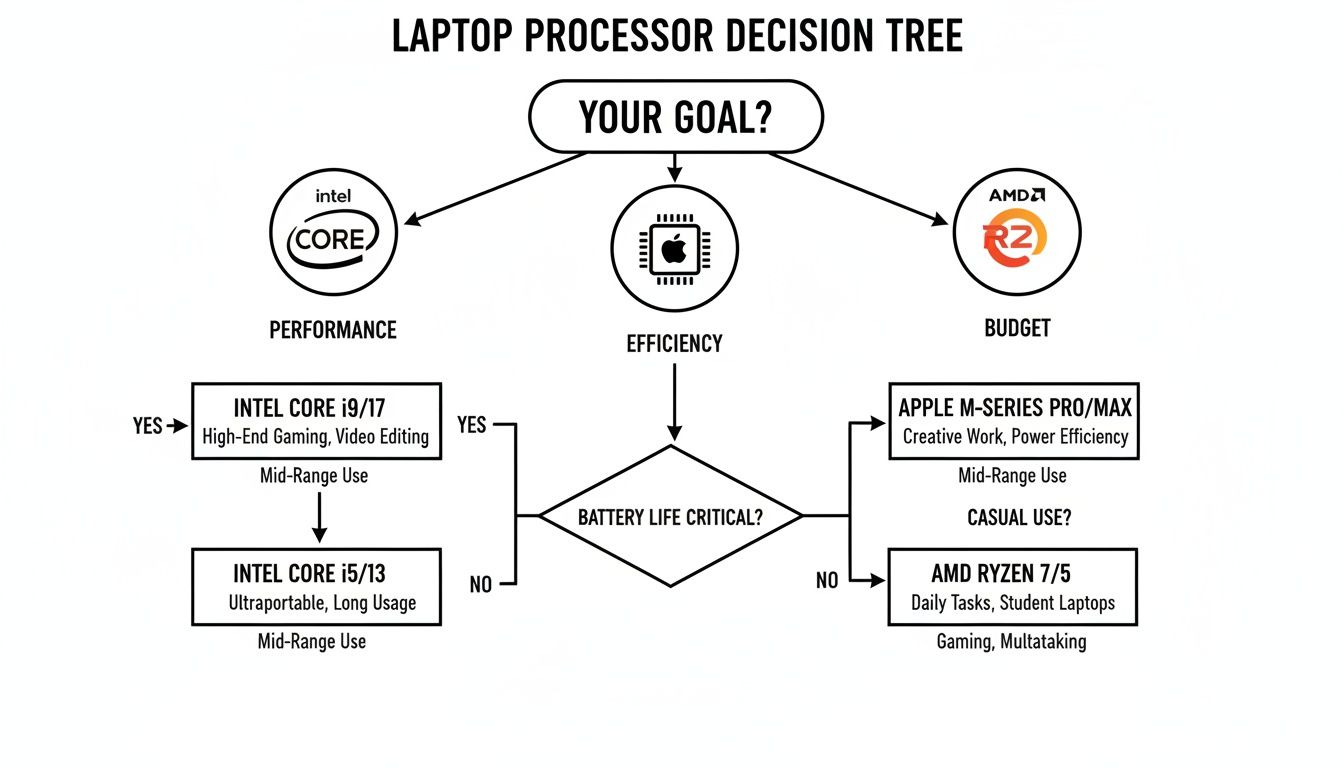
As you can see, it simplifies that initial choice by framing Intel for performance, Apple for efficiency, and AMD for budget-friendly power, guiding you toward the ecosystem that's likely the best fit.
For the Everyday Web Browser and Student
If your laptop is basically a portal for browsing the web, streaming videos, firing off emails, and working on documents in Microsoft Office or Google Docs, you don’t need a beast of a processor. What you do need is snappy responsiveness for light tasks and great battery life.
- What Matters Most: A respectable base clock speed makes apps feel quick to load, and having at least four cores helps the system handle background processes without stuttering.
- Processor Recommendations: An Intel Core i3 or AMD Ryzen 3 will deliver a perfectly smooth experience for these activities. If all-day battery and a fluid operating system are your top priorities, an entry-level Apple M-series chip is a brilliant, though more expensive, alternative.
For the Business Professional and Multitasker
The modern workday often means juggling a dozen things at once. We're talking video calls, massive spreadsheets, countless browser tabs, and presentation software all running simultaneously. A work laptop's processor has to handle this constant multitasking without breaking a sweat. This has become non-negotiable as laptops have replaced desktops as the primary work tool for so many of us.
Back in 2018, laptops already made up around 33% of all business hardware in the Netherlands, with a staggering 81% of businesses with 50+ employees using them. This massive shift away from desktops shows just how much laptop processors have improved, becoming powerful enough for demanding professional workflows. You can dive deeper into this trend in the detailed report on Dutch hardware trends.
- What Matters Most: A higher core and thread count is non-negotiable. Look for at least 6 cores and 12 threads to keep multitasking fluid. Good single-core performance is also key for keeping individual applications feeling responsive.
- Processor Recommendations: An Intel Core i5/i7 or an AMD Ryzen 5/7 is the sweet spot here. These chips strike a fantastic balance between multi-core strength for juggling tasks and single-core speed for everyday snappiness.
For the Content Creator and Developer
This is where processor performance becomes absolutely critical. Tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, graphic design, and code compilation can bring a lesser CPU to its knees. For these users, every extra bit of processing power directly translates into time saved and less frustration.
- What Matters Most: Maximum cores and threads. Simple as that. These heavy workloads are designed to use every ounce of processing power you can give them. A high clock speed and a large cache also play a huge role in cutting down render times and keeping your workflow smooth.
- Processor Recommendations: An Intel Core i7/i9 (H-series) or an AMD Ryzen 7/9 (H-series) are the go-to choices for raw power. Apple's M-series Pro and Max chips are also exceptional contenders, offering incredible performance combined with remarkable power efficiency—a game-changer for creative work on the move.
For the Passionate Gamer
Gaming is a unique beast, putting intense demands on both the CPU and the GPU. The processor in a gaming laptop handles all the game logic, physics, and AI, and it has the crucial job of feeding the graphics card a constant stream of information to render frames. If it can't keep up, you get stutter and lag.
- What Matters Most: High single-core clock speed is king. While more cores are becoming important for modern games, many titles still lean heavily on the raw speed of one or two cores to push out the highest possible frame rates. A large cache also provides a noticeable benefit.
- Processor Recommendations: Look for an Intel Core i5/i7 or AMD Ryzen 5/7 from their high-performance "H" or "HX" series. These chips are specifically designed with higher TDPs to sustain blazing-fast clock speeds under load, preventing performance from dipping during those intense gaming moments.
Your Checklist for Choosing the Right Processor
Picking the right processor for a new laptop can feel like wading through an alphabet soup of model numbers and marketing jargon. It's overwhelming. But it gets a whole lot simpler when you have a clear plan.
Forget trying to find the single "best" processor on the market. That's a fool's errand. The real goal is to find the one that hits the sweet spot between performance and price for you. This checklist will help you cut through the noise and make a smart, confident decision by focusing on what you actually need.
Let’s walk through the steps to make sure you’re investing in power you'll genuinely use.
Step 1: Define Your Primary Tasks
First things first, be brutally honest about how you'll use this laptop 90% of the time. Are you a student who lives in a web browser and a word processor? Or are you a creative professional who spends all day in demanding software like Adobe Premiere Pro?
- Light Use: If your world revolves around web browsing, streaming video, and office apps, you don't need to overspend. A processor with solid single-core speed and at least four cores will feel perfectly snappy for these tasks.
- Moderate Use: Are you a heavy multitasker? Juggling video calls, massive spreadsheets, and dozens of browser tabs all at once? If so, prioritise a higher core and thread count—aim for at least 6 cores/12 threads.
- Heavy Use: This is the territory of content creators, software developers, and serious gamers. You need all the power you can get. Target processors with the highest core counts, fastest clock speeds, and largest caches your budget can handle.
Step 2: Set a Realistic Budget
Your budget is the great filter. Processors are often the biggest single factor driving a laptop's price, so knowing your spending limit from the start helps you focus on the right tier of performance. Don't just look at the total price tag; compare different laptops within your price range to see which one packs the better CPU.
A classic mistake is paying a premium for a top-of-the-line chip when a mid-range option would have been more than enough. For instance, a modern Ryzen 5 can often deliver fantastic multi-core performance that rivals older, much more expensive chips, offering incredible value.
Pro Tip: Before you buy, look up reviews that benchmark different CPUs within your specific budget. This data-driven approach often uncovers hidden gems and stops you from overpaying for a brand name when a competitor offers better performance for less.
Step 3: Identify Key Performance Indicators
Now that you know your tasks and your budget, you can zero in on the specs that actually matter for your needs. This is where you connect the "why" with the "what."
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- For General Responsiveness: Focus on a processor from a recent generation with a good base and boost clock speed. This keeps everyday tasks feeling quick.
- For Heavy Multitasking: Prioritise a higher core and thread count. For multitasking, more is almost always better.
- For Gaming: Look for high clock speeds (especially the single-core turbo) from a manufacturer's high-performance line (like Intel's H-series).
- For Battery Life: Check the processor's TDP. A lower wattage (like you'll find in U-series chips) generally means longer battery life, which is crucial if you're always on the move. And to keep your device powered up on the go, check out our guide on the best power banks for laptops with USB-C.
By following this three-step process, you turn a complex technical choice into a series of simple, practical questions. You'll sidestep the marketing hype and land on a processor that perfectly aligns with your daily workflow, ensuring your new laptop is an investment that truly pays off.
Answering Your Top Processor Questions
Even after you’ve got a handle on cores, clock speeds, and the big brands, a few practical questions always seem to surface right when you’re about to make a choice. This section is all about tackling those common queries head-on, giving you clear, straightforward answers to help you lock in your decision with confidence.
Think of this as the final piece of the puzzle. We'll clear up any nagging doubts about things like processor generations, whether you can upgrade later, and what those confusing model numbers actually mean. The goal is to leave you with a complete and practical understanding of what makes a great laptop processor tick.
Can I Upgrade My Laptop Processor?
For almost every modern laptop out there, the answer is a firm no. It's a fundamental difference from desktop PCs, where the CPU is a separate component you can pop out of a socket. In a laptop, the processor is almost always soldered directly onto the motherboard.
This isn't just to make things difficult; there are solid engineering reasons for it:
- Saving Space: Soldering the CPU shaves off precious millimetres, which is what allows for the incredibly thin and light designs we love in today's ultrabooks.
- Cooling Efficiency: A direct connection to the motherboard is much better for getting heat away from the chip—a constant battle inside a cramped laptop chassis.
- System Stability: It guarantees a perfect, factory-tested connection between the processor and all the other critical bits and pieces on the board.
Because the processor is essentially a permanent fixture, it's not designed to be swapped out by a user. Trying to do so would require highly specialised desoldering equipment and would absolutely void your warranty, not to mention risk frying the entire machine.
This reality brings home a crucial point: you have to choose the right processor from day one. Since you can't upgrade it later, the CPU you buy is the one you’re stuck with for the life of the laptop.
Do Processor Generations Really Matter?
Yes, they matter immensely. In fact, a processor's generation is often a more important indicator of performance than its model name (like a Core i5 versus a Core i7). Each new generation brings significant improvements in architecture, which means the chip can get more work done in every single clock cycle.
Think of it this way: imagine two cars with engines that spin at the exact same RPM. The newer car's engine is just designed better—it's more efficient, so it generates more horsepower from the same number of rotations. Processors are exactly the same. A 13th-generation Intel Core i5 will almost always run circles around a 10th-generation Core i7, both in raw speed and power efficiency, even though the "i7" name sounds more powerful on paper.
When you're shopping, always try to get the newest generation you can afford. It’s the simplest way to ensure you're getting better overall performance, longer battery life, and support for the latest features.
Understanding U-Series vs H-Series Processors
You'll often spot letters like 'U' or 'H' tacked onto the end of a processor's model number. These letters tell a vital story about the chip's real purpose and how much power it's designed to draw. This is one of the most practical things to understand when picking a laptop.
U-Series (Ultra-Low Power): These are the efficiency champions. Built with a low TDP (around 15W), they're designed to sip power, giving you fantastic battery life in a slim, lightweight laptop. They are perfect for everyday tasks like browsing, office work, and watching videos, but they'll start to choke on heavy, sustained workloads like video rendering.
H-Series (High Performance): These are the powerhouses. With a much higher TDP (typically 45W or more), these chips are all about raw speed and sustained muscle. You’ll find them in beefy gaming laptops and mobile workstations, where they can chew through demanding jobs like 3D modelling, compiling code, or playing the latest games. The trade-off? Much shorter battery life and a heavier laptop with a serious cooling system.
The Netherlands is a key player in the global movement of these devices. In 2023, the country was both the 6th largest exporter ($15 billion) and 4th largest importer ($14.3 billion) of computers. This showcases its role as both a major distribution hub and a powerful market for high-performance and everyday laptops. You can dig into more of this data on the Netherlands' computer trade dynamics on oec.world.
Is Integrated Graphics Good Enough?
For years, "integrated graphics" was a dirty word among tech enthusiasts. It had a reputation for being weak, barely able to handle anything beyond showing your desktop. That reputation is completely outdated. Modern integrated graphics, like Intel's Iris Xe and AMD's Radeon solutions, are surprisingly powerful.
For the vast majority of people—students, office workers, and even casual content creators—today's integrated graphics are more than enough. They can easily handle:
- Flawless 4K video playback.
- Powering multiple high-resolution monitors.
- Light photo editing and graphic design work.
- Casual gaming, especially with older or less demanding titles.
You only really need a dedicated graphics card (GPU) if you're a serious gamer who wants to play the latest AAA titles at high settings, a professional 3D artist, or a video editor working with complex visual effects and high-resolution footage. For just about everyone else, the capable integrated graphics built into modern CPUs will serve you perfectly well.
At People & Media B.V., we believe that understanding the tools you use is the first step toward unlocking your full potential. Whether you're a creator, a professional, or a lifelong learner, our curated resources are here to help you gain wisdom and grow. Discover more insights on our platform at https://www.peopleandmedia.com.








Responses