Exploring the Untapped Potential of Natural Resources in Greenland
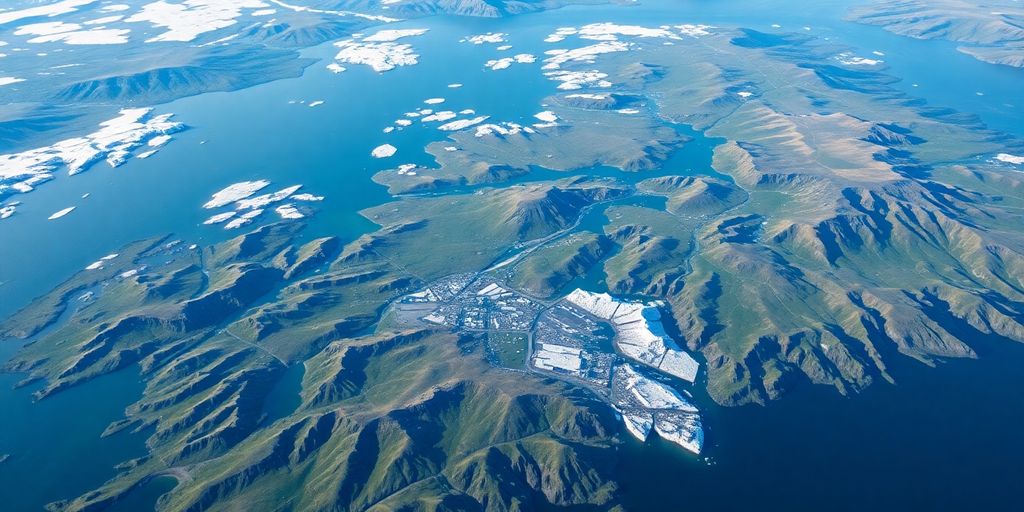

Greenland’s natural resources have long been overlooked, but the island holds a treasure trove of minerals vital for modern technology. While countries like Canada and Australia have tapped into their geological wealth, Greenland’s mining efforts remain small-scale. This article explores Greenland’s potential to become a major player in the global resource market, examining the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Greenland is rich in minerals like rare earth elements, graphite, and niobium, crucial for the green transition.
- Compared to Canada and Australia, Greenland’s mining activities are limited, but the potential is vast.
- The harsh climate and difficult terrain pose significant challenges to mining operations in Greenland.
- Investment opportunities in Greenland are growing, but infrastructure and regulatory hurdles remain.
- Technological advancements could aid in unlocking Greenland’s resource potential, making mining more sustainable.
The Rich Geological Landscape of Greenland
Understanding Greenland’s Geological History
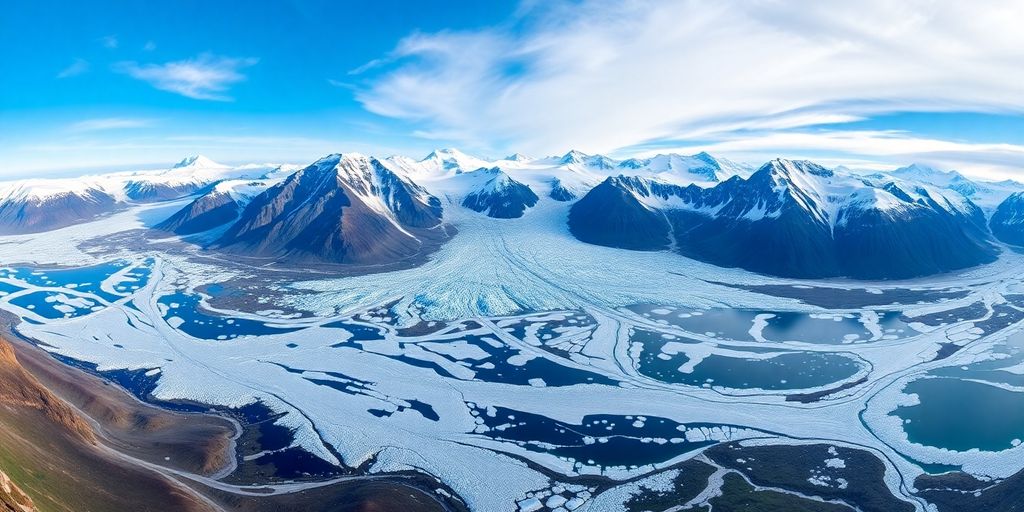
Greenland’s geological history is like a giant puzzle waiting to be pieced together. This vast island has seen a complex geological evolution over millions of years. Greenland’s geological past is marked by the formation of ancient rocks, some of which are among the oldest on Earth. These rocks tell stories of tectonic shifts, volcanic activity, and the presence of ancient oceans. The island’s geological timeline includes periods of intense volcanic activity, which have left behind rich mineral deposits. As the ice recedes, more of this geological history is revealed, offering a glimpse into the Earth’s distant past.
Comparing Greenland’s Geology to Canada and Australia
When you look at Greenland’s geology, it’s hard not to draw comparisons to places like Canada and Australia. These countries are known for their rich mineral resources and extensive mining activities. But Greenland is still mostly untapped. Both Canada and Australia have similar geological features, such as ancient cratons and mineral-rich belts. However, Greenland’s harsh climate and ice coverage have kept its resources largely hidden. As more ice melts, the potential for discovering valuable minerals increases, making Greenland an exciting prospect for future exploration.
The Role of Ice-Free Land in Resource Exploration
The ice-free areas of Greenland are crucial for resource exploration. These regions are like windows into the island’s geological wealth. As the ice retreats, it exposes new land that could hold significant mineral deposits. The challenge, though, is that Greenland’s terrain is tough to navigate, and the climate can be unforgiving. But with modern technology and a growing interest in sustainable mining, there’s a real opportunity to explore these ice-free zones. This could lead to the discovery of critical raw materials that are essential for the green transition, such as rare earth elements and other valuable minerals.
Critical Raw Materials: Greenland’s Hidden Treasure

Rare Earth Elements and Their Importance
Greenland is sitting on a treasure trove of rare earth elements (REEs), which are key to the tech world. These elements are crucial for making everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. Greenland’s potential to supply these materials could change the global market, reducing reliance on traditional suppliers. The country’s unique geological history has set the stage for these deposits, making it a hotspot for future exploration.
Exploring Greenland’s Graphite and Niobium Deposits
Graphite and niobium are two more critical materials found in Greenland. Graphite is essential for battery technology, while niobium is used in steel production to improve strength and flexibility. Greenland’s deposits of these materials are largely untapped, presenting a huge opportunity for mining companies.
- Graphite is vital for lithium-ion batteries.
- Niobium enhances steel’s durability and resistance.
- Both materials are pivotal for advancing green technologies.
Potential of Platinum Group Metals in Greenland
The platinum group metals (PGMs) in Greenland are another hidden gem. These metals, including platinum and palladium, are used in catalytic converters and other industrial applications. The potential for large-scale mining of PGMs in Greenland could position the country as a major player in these markets.
Greenland’s geological landscape is like an open book, waiting to be read by those willing to explore its depths. The promise of critical raw materials offers a path to economic growth and technological advancement.
Challenges in Greenland’s Mining Sector
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
Greenland is in a tricky spot, balancing the need to protect its environment while also wanting to cash in on its mineral wealth. The government has been careful, setting up rules and protections, but there’s still a long way to go. Investors find the changing regulations a bit of a headache, making them hesitant. On the bright side, there’s hope that things are getting more stable and clearer.
Infrastructure and Accessibility Issues
Mining in Greenland is no walk in the park. The place is huge, and a lot of it is covered in ice. Getting to the mineral-rich areas is tough, and setting up the infrastructure needed for mining is even tougher. Roads, ports, and other facilities are often lacking, making the cost of mining sky-high. This lack of infrastructure makes investors think twice before diving in.
Impact of Harsh Climate on Mining Operations
The weather in Greenland is no joke. With freezing temperatures, snowstorms, and long periods of darkness, mining operations face serious challenges. Equipment needs to be tough enough to withstand the harsh conditions, and workers have to be prepared for the extreme environment. This climate factor adds another layer of difficulty to mining projects, making them more expensive and risky.
Greenland’s journey to become a major mining hub is fraught with obstacles. These challenges, from regulations to climate, need careful navigation to unlock the island’s full potential.
Investment Opportunities in Greenland’s Natural Resources
Greenland, with its vast and largely unexplored mineral wealth, presents a unique opportunity for investors. Despite some concerns about the country’s inexperience in mineral resource monetization, there’s a rich history of mining here. The potential for critical raw materials, like rare earth elements, is immense. Investors with a long-term vision might find Greenland’s mineral resources too appealing to ignore. However, challenges such as harsh climate conditions, limited infrastructure, and a complex tax regime, which includes high mineral royalties, can dampen enthusiasm. Yet, for those willing to take the plunge, the rewards could be significant.
- High mineral royalties: 5.5% on gemstones, 5% on rare earth elements, 2.5% on other minerals.
- Additional tax burdens: Surplus royalty on profits over 40%, with rates of 3.75%, 8.75%, and 15%.
- Greenland’s vast ice-free land blocks offer significant exploration potential.
Greenland’s journey towards becoming a mining powerhouse is marked by cautious regulation and a commitment to environmental safeguards. The government is keen on creating an attractive investment climate while ensuring sustainable development.
Efforts to attract Chinese investment in Greenland’s mining projects have so far seen limited success. The perception of Greenland as a challenging investment environment, coupled with China’s control over critical mineral prices, has contributed to this hesitance. However, Greenland’s potential in critical mineral resources remains vast, and as global demand tightens, interest may grow. The Greenland Mineral Resources Portal is a valuable tool for investors, offering comprehensive data on the country’s geology and mineral potential.
Greenland is taking steps towards sustainable mining practices, which could enhance its appeal to environmentally-conscious investors. The government is implementing regulatory reforms aimed at balancing economic growth with environmental protection. This includes promoting transparency and informed decision-making through resources like the Greenland Mineral Resources Portal. As the world shifts towards renewable energy and sustainable development, Greenland’s commitment to responsible mining could become a significant draw for global investors.
The Future of Large-Scale Mining in Greenland
Government Strategies for Mining Development
Greenland’s government has been cautiously optimistic about the potential for large-scale mining. They’ve been working on creating a balanced regulatory framework that encourages investment while safeguarding the environment. This approach aims to make Greenland an attractive destination for mining companies. However, challenges remain, especially in terms of infrastructure and the harsh climate.
Potential for Oil and Gas Exploration
While there is significant interest in Greenland’s oil and gas potential, commercial production is not expected for at least another decade. The harsh conditions and high extraction costs make it a challenging endeavor. Yet, the long-term outlook remains positive as technological advancements could make extraction more feasible.
Balancing Economic Growth with Environmental Protection
Greenland faces the tricky task of balancing economic growth through mining with environmental preservation. The government is focused on sustainable practices to ensure that mining activities do not harm the pristine environment. This balance is crucial for maintaining the trust of the local population and global investors alike.
Technological Advancements in Greenland’s Resource Exploration
Innovations in Geological Mapping
Geological mapping in Greenland is getting a tech boost. With advanced tools and methods, scientists can now map the island’s vast terrain more accurately. This technology is crucial for identifying potential mining sites. New software helps geologists create detailed maps that show even the smallest mineral deposits. These maps are essential for companies looking to invest in Greenland’s resources.
The Use of Remote Sensing Technologies
Remote sensing technologies have changed the game for exploring Greenland’s resources. Satellites and drones can capture images of the land, revealing hidden mineral deposits. Remote sensing is especially useful in Greenland’s harsh climate, where on-the-ground exploration is tough. These technologies allow for a broader view, helping to pinpoint areas with the highest potential for mining.
Advancements in Sustainable Mining Practices
Sustainable mining is a big deal in Greenland. New technologies make it possible to mine resources while minimizing environmental impact. Companies are using eco-friendly methods to extract minerals, ensuring that Greenland’s natural beauty is preserved. These advancements not only protect the environment but also make mining operations more efficient.
Greenland is on the brink of a mining revolution. With cutting-edge technology, the island can unlock its vast mineral wealth responsibly, paving the way for economic growth.
Greenland’s Path to Economic Independence Through Resource Utilization

The Role of Natural Resources in Economic Self-Sufficiency
Greenland is sitting on a treasure trove of natural resources that could pave the way to economic self-sufficiency. With vast deposits of minerals like rare earth elements, graphite, and niobium, the island holds the potential to significantly boost its economy. Developing these resources could lessen the reliance on Denmark, inching Greenland closer to economic independence.
Challenges in Reducing Dependency on Denmark
While the potential is immense, Greenland faces hurdles in cutting its economic ties with Denmark. The harsh climate, limited infrastructure, and regulatory hurdles make mining operations complex and costly. Furthermore, Greenland’s political landscape can be unpredictable, adding another layer of difficulty for investors.
Strategies for Long-Term Economic Growth
To achieve long-term growth, Greenland must focus on sustainable mining practices and attract global investments. This involves creating a stable regulatory environment and improving infrastructure to support mining activities. Encouraging foreign investments, particularly from countries like China, could also play a crucial role in developing Greenland’s mining sector. However, it’s essential to balance these efforts with environmental protection to ensure the preservation of Greenland’s unique ecosystem.
Greenland’s journey to economic independence is akin to navigating uncharted waters. While the path is fraught with challenges, the promise of self-sufficiency through resource utilization is a compelling vision for the island’s future. The key lies in strategic planning and responsible management of its abundant natural resources.
Conclusion
Greenland’s natural resources hold a world of possibilities, just waiting to be tapped. The island’s vast mineral wealth, including rare earth elements and other critical materials, is a beacon for future development. Yet, challenges remain. The harsh climate, limited infrastructure, and regulatory hurdles have kept many investors at bay. But as global demand for these resources grows, Greenland’s potential becomes harder to ignore. With careful planning and sustainable practices, Greenland can transform its untapped resources into a thriving industry, benefiting both its economy and the global market. It’s a journey that requires patience and perseverance, but the rewards could be immense.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes Greenland’s geology unique?
Greenland’s geology is unique because it has a long and varied geological history. It is similar to countries like Canada and Australia, which are known for extensive mining activities. However, Greenland’s mining has been limited and small-scale.
Why are rare earth elements important?
Rare earth elements are important because they are used in many high-tech products, like smartphones, electric cars, and wind turbines. They are crucial for the green transition and modern technology.
What challenges does Greenland face in mining?
Greenland faces challenges like harsh climate, difficult terrain, limited infrastructure, and the need for more geological mapping and data collection. These factors make mining operations tough.
How is Greenland trying to attract investors?
Greenland is trying to attract investors by improving its regulatory framework, ensuring environmental safeguards, and promoting transparency. They are also working on better infrastructure and accessibility.
What role does China play in Greenland’s mining sector?
China has shown interest in Greenland’s mining sector, but so far, there has been little significant investment. Greenland is looking to attract more international investors, including Chinese companies.
How can Greenland achieve economic independence?
Greenland aims to use its natural resources to become economically self-sufficient. This involves reducing dependency on Denmark and developing sustainable mining practices to ensure long-term growth.







Responses